One of the most significant concerns of the pharmaceutical industry is proper medication storage. Pharmaceutical products need to be kept within a specific range of temperature and moisture levels. Outside of these conditions, medications may not maintain their integrity, with active ingredients degrading over time. Pharmacies can preserve their products’ integrity through appropriate storage techniques. Learn how to manage pharmacy room temperature with the aid of temperature sensors below.
Temperature Control and Pharmaceutical Drug Storage
Most medications need to be stored in a dry, dark and cool place. High temperatures can chemically alter medications, while high moisture can cause tablets to degrade. Most prescription medications are stored in one of four types of conditions:
- Room temperature: Most medications are designed to be stable at room temperature, so this is a common storage requirement. Room temperature for pharmaceuticals is defined as 20 to 25 degrees Celsius or 68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Cool storage: Cool storage conditions are defined as 8 to 15 degrees Celsius or 46 to 59 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Cold storage: Cold storage is considered 2 to 8 degrees Celsius or 36 to 46 degrees Fahrenheit. These conditions are optimal for inhibiting chemical reactions and microbial growth. Cold storage is often required for highly degradable drugs and vitamins.
- Fridge storage: Fridge storage is another common pharmaceutical storage requirement and is defined as -4 to 2 degrees Celsius or 25 to 36 degrees Fahrenheit.
Many manufactures recommend discarding medications if they are stored outside their recommended temperature range for five hours or more. Exposure to higher temperatures can result in the active chemicals in medications changing at a molecular level. Sometimes, this can result in the medication decomposing, making it less potent or even changing its effects. Medications known to be affected by temperatures include injectable diabetes treatments, eye-drop medications, inhaled drugs, birth control and various antibiotics. Degraded medications can be life-altering or life-threatening, so they must be stored properly.
Best Practices for Pharmaceutical Drug Storage
It’s easy for individuals to expose their medications to heat and humidity accidentally — a hot car ride or an open bathroom medicine cabinet is often all it takes. But heat exposure can also occur in a pharmacy. Power outages, heatwaves and malfunctioning equipment can all result in heat exposure within a pharmacy building and destroy pharmaceutical supplies. To protect against temperature exposure, pharmacies can employ a few best practices:
- Packaging: Ensure medications are packaged properly, complete with suitable coverings and seals. Avoid opening new packages unless necessary and double-check that containers are adequately sealed when not in use.
- Airflow: Proper airflow can help dissipate heat within a pharmacy. To this end, take advantage of windows and air vents. Make sure screens are installed to prevent bugs from entering the pharmacy and leave windows open when possible. Try to circulate this airflow as much as possible using fans.
- Placement: Tightly packed boxes and shelves can trap heat, causing medications to overheat over time. Place shelves and boxes in the pharmacy so there is enough room for air to flow between them.
- Air conditioning: Always ensure your pharmacy has a functioning air conditioner available to handle particularly hot days. Schedule regular maintenance for your air conditioning system to ensure it is properly functioning at all times.
On top of these best practices, implementing a temperature monitoring system can help ensure that medications are stored at proper temperatures.
The Role of Temperature Monitoring Systems
Monitoring temperatures and conditions manually is a common method for maintaining pharmacy room temperature range. This manual recording can be inconsistent or inaccurate. It is also limited to working hours when someone is present in the pharmacy to record temperatures. As an alternative, many pharmacies have turned to automated temperature monitoring systems.
Temperature monitoring systems use wireless sensors to record environmental conditions in a space. Using a wireless network, these sensors can monitor the temperature in a pharmacy storage area, sending records to a database. Some systems can also measure humidity. The system sends automated alerts when a space’s measurements fall outside set thresholds so someone can quickly come and resolve the problem before medications are negatively affected.
Radio Bridge, a MultiTech brand, offers a range of temperature monitoring sensors that can be used in pharmacies. Based on LoRaWAN® wireless technology, these sensors provide wireless penetration through walls and floors and have excellent range. They can also be configured remotely. If measurements fall above or below preset thresholds, the sensors use the system to send out an alert.
Radio Bridge sensor options include:
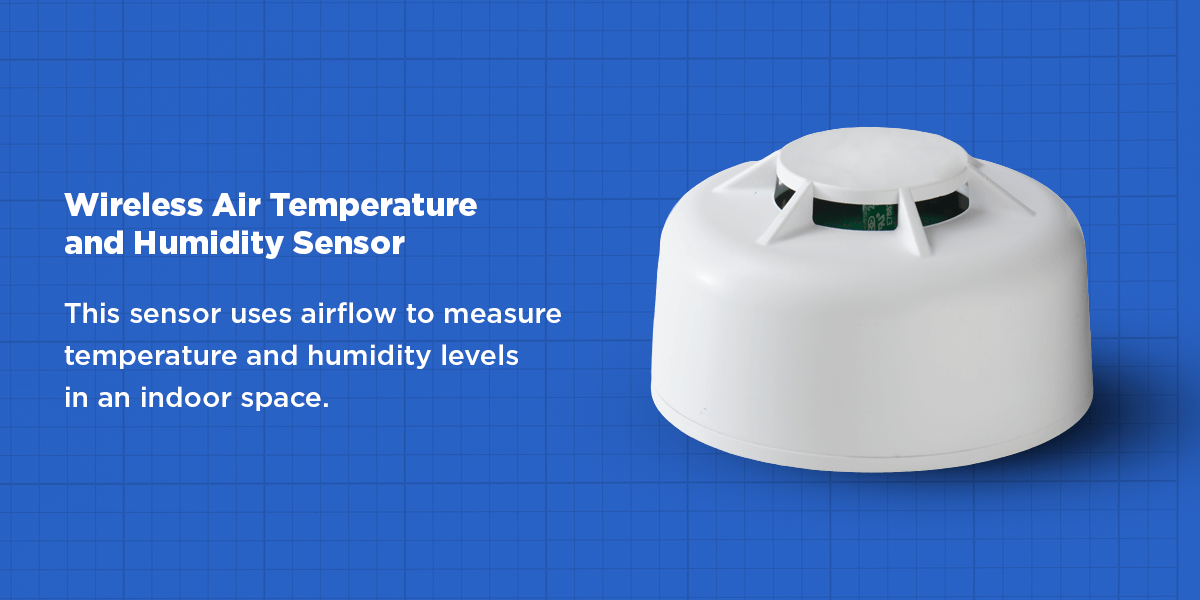
- Wireless Air Temperature and Humidity Sensor: This sensor uses airflow to measure temperature and humidity levels in an indoor space.
- Wireless IP67 Air Temp and Humidity Sensor: This external probe sensor uses a porous stainless steel filter to measure humidity and temperature using airflow. This sensor is rated to be used in both outdoor and industrial environments, with an IP67-rated enclosure and cable and an IP54-rated filter.
- Wireless No-Probe Temperature Sensor: This probeless temperature sensor measures the temperature of the air around the sensor.
- Wireless Thermocouple Temperature Sensor: The wireless thermocouple temperature sensor uses an external thermocouple to measure temperatures. This sensor can be configured with a variety of thermocouple types, including B, E, J, K, N, R, S and T. It also features an IP67 weatherproof enclosure, making it suitable for both outdoor and industrial use.
- Wireless IP67 External Probe Temperature Sensor: The external probe temperature sensor uses an external probe to measure temperature. It features an IP67-rated enclosure, making it useable for outdoor and industrial uses.
- Wireless External Probe Temperature Sensor: This external probe temperature sensor uses an external probe for temperature measurement and is ideal for low-cost indoor applications.
Contact Radio Bridge for Temperature Monitoring Solutions
Temperature monitoring is a necessity for the storage of antibiotics and other medications. If you’re looking for a temperature monitoring product to help with pharmacy storage management, Radio Bridge has solutions to help.
At Radio Bridge, we design and produce long-range wireless sensors for various industries. Our sensors are designed with the LoRaWAN wireless standard to ensure reliability and signal strength, making them an ideal choice for a variety of applications.
Our temperature sensors are an excellent choice for the pharmaceutical industry, with a range of options to handle practically any environment and monitoring need. Our sensors are linked to our convenient web-based console, which serves as a hub where you can set up sensor configurations and alerts, monitor activity and enjoy other features.
Contact Radio Bridge today to learn more about our temperature monitoring solutions.